Cyber security for mobile networks: What’s the big deal? - ETTelecom.com
Cyber security for mobile networks: What’s the big deal? - ETTelecom.com |
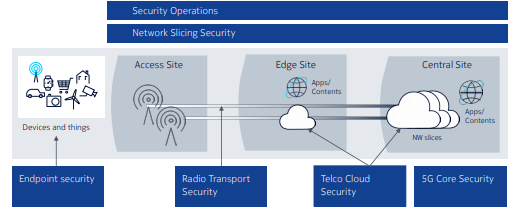
| Cyber security for mobile networks: What’s the big deal? - ETTelecom.com Posted: 28 May 2021 12:19 AM PDT  By Randeep Raina, CTO, Nokia India By Randeep Raina, CTO, Nokia IndiaIn today's digital world, where the internet has become a part of life, growing digitalization and networking has also seen incidents of cybercrime and data breach becoming more and more common. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect. India ranks amongst some of the most cyber attacked countries in the world. As per the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, there have been close to 7 lakh cyber-attacks reported in the country in 2020 (till Aug). Importance of digital trust and key attributesCSPs are relying on 5G to generate new revenue streams by offering new/ innovative services to end consumers, enterprises, and businesses. Their success depends partly on their ability to build 'digital trust' in the eyes of their customers by ensuring that their confidential enterprise or personal data is safe. The security needs will vary with the user and type of service, for example, the security needs of a retailer will be different from those of an enterprise, e.g., financial organization. 5G will allow connecting millions and millions of new IoT end points and devices to the network. The lagging security protection of many IoT devices can offer the opportunities for launching cyber-attacks through a much greater number of access points. Adaptation, speed, integration and automation have emerged as the key attributes for 5G security. A flexible and adaptive 5G security solution will be needed to be able to respond to the sophisticated cyber-attacks. Integrated security solutions complemented by technologies like AI/ ML, analytics and automation can quickly spot the threat and alert the security apparatus for swift and timely action. Delivering end to end security5G architecture is broadly built up of Distributed/ Cloud RAN, Edge Core and Cloud Core. End-to-end security, from the mobile core to the edge of the network to end point devices, is vital to protect the network and associated services. 5G standards were developed on the principle of 'Secure by Design'- more security features were included in the standards so as to offer an inherent higher level of protection on network level to consumers and networks. 3GPP 5G standards can meet the security needs to a great extent within the 5G network, but the situation can be different once the device or application connects to the internet. Fig. 1: Each 5G network component has its own security requirement 5G relies on techniques such as mutual authentication, signed software delivery from a trusted source to ensure authenticity, certificates, keys and encryption to manage endpoint security. Further, analysing traffic patterns to detect anomalies using artificial intelligence, firmware upgrade and traffic throttling also help to minimize the risks significantly. Radio and transport security 5G base station can be securely bootstrapped by CSP-run Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for authentication, encryption and integrity to protect traffic against manipulation and eavesdropping. Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is used to protect the communication between the RAN and core network. Telco cloud security Protecting and assuring the integrity of the virtualization layer and overall cloud platform software requires robust, security-aware implementation of the VNFs including physical separation where needed Further, virtual firewalls help to provide perimeter security and network internal traffic filtering, while security zones can be logically and/or physically separated. Selected traffic and stored data can also be protected by encryption. 5G core network security Another key aspect is to provide security at the main entry and exit points, for example, N2 interfaces at AMF or N32 at SEPP. Network slicing Network slicing allows to efficiently provision of different levels of performance and security to users of different services/ slices at scale. For example, an isolated network slice can be created to minimize the risk of confidential enterprise or personal data being leaked. Each network slice spans the device, radio, access, transport and core, to the application servers in a data centre - security must be designed, provisioned, audited, managed and reported continuously end-to-end. Security operations with SOAR and Nokia offering Effective security operations are based on tools that meet the performance demands of virtual networks and support other requirements, such as elastic scaling. The key principles of Security Orchestration, Analytics and Response/Reporting (SOAR) include:
Nokia's integrated security offering covers the complete 5G solution, including radio, transport, core, telco cloud, IoT and devices, and network slicing. The entire cycle of security is covered - assessment, prevention, detection and response. Whether a CSP wants to keep security operations in-house or outsource that to a trusted partner, Nokia provides the services and solutions needed to build trust in the 5G era. Nokia's security offering is complemented by its unmatched track record in ethical behaviour- recognized as one of the World's Most Ethical Companies in 2021- fourth consecutive year and for fifth time overall. |
| Encrypted messages don't always stay private. Here's what that means for you - CNET Posted: 08 Oct 2020 12:00 AM PDT  Encrypted messaging locks down your chats -- but only while they're traveling to the recipients. Angela Lang/CNETAs a group of alleged conspirators recently learned, encrypted messaging isn't a guarantee that your private conversations will stay between you and the recipient. The FBI arrested six men on Thursday for allegedly plotting to kidnap Michigan Gov. Gretchen Whitmer. How did the feds get the information they needed? They read the group's encrypted conversations. To be clear, accessing the communications wasn't a highly technical effort. The FBI had a confidential informant who participated in the group message threads in which much of the conspiracy was laid out, according to a criminal complaint. That kept the FBI in the loop even when the group changed messaging apps to avoid detection. "Because the group still included [the informant], the FBI has maintained the ability to consensually monitor the chat communications," FBI special agent Richard J. Trask II said in the complaint. The incident underscores a basic fact about encrypted messaging apps, like Signal, Telegram and WhatsApp. While they all offer a layer of privacy, there are plenty of ways for someone to access your messages from these services. That's good news and bad news. On the bright side, it means criminals plotting violence can't rely completely on encrypted messaging services to hide their plans from the police. While law enforcement has warned that encryption threatens to make their investigations into the worst criminals "go dark," this case is one example of how investigators can continue to read messages sent with encrypted services. On the other hand, it means regular users who want to protect their data from hackers, creeps and foreign governments need to rethink what encrypted messaging really does for them. It isn't a magic wand. Here's what you should know about what encryption does -- and doesn't do -- to protect your privacy. How does encrypted messaging work?It's OK, most people don't have a handle on just what encrypted messaging apps like Signal, Telegram and Facebook-owned WhatsApp do. They look and act like regular text messaging tools. But behind the scenes, the services scramble up your messages as they travel across cellular communications systems and the internet to get to the intended recipient's phone. That means no one involved in sending the message -- including the encrypted messaging service -- can read your messages. Regular SMS messaging is sent in plaintext and doesn't have this layer of protection, so your SMS messages are vulnerable to interception at multiple points as they travel from your phone to the recipient's device. Is my phone encrypted, too?If you use an iPhone, the data on your phone is encrypted when the device is locked. On Android phones, users have to enable disk encryption themselves. Device encryption will protect your messages as long as the phone is locked. Apple describes this form of encryption as essential to users' privacy. For one thing, it protects all the personal data on your phone if it gets stolen. Think private messages and photos, as well as access to your email account and financial information. Like encrypted messaging, device encryption has been a sore subject with law enforcement. The FBI tried to get a court order in 2016 to force Apple to help it access encrypted messages on an iPhone used by an extremist shooter. After Apple refused, the agency was eventually able to access the data on the phone with another technique. How can someone get my encrypted messages?As the Michigan case shows, anyone you send a message can share it with a wider circle of people, regardless of whether it's sent on an encrypted service. The same goes for anyone who has the ability to unlock your phone, which disables device encryption. If you don't lock your device at all, anyone who gets your phone can access your messages. Then there's hacking, which is used by law enforcement, as well as criminals and foreign governments, to target someone's phone with malicious software. Once the device is compromised, the malware can read messages on the device just like someone looking over your shoulder to watch you type. These tools are sophisticated, can be very expensive, and require someone to target you specifically. Another form of malware that can get your communications is called stalkerware. That's phone monitoring software that many people admit to using to spy on their partners or exes, and it usually requires the person to have access to your phone. There are steps you can take if you're worried your device has stalkerware. Finally, there are your backups. Data on your cloud accounts might not be encrypted, and anyone who has the password could access your backed-up messages there. Some stalkerware works by accessing your phone's cloud backup. That's a great argument for using a unique, hard-to-guess password to protect your cloud accounts, and using a password manager. |
| You are subscribed to email updates from "mobile encryption app,samsung note 5 encryption,data encryption meaning" - Google News. To stop receiving these emails, you may unsubscribe now. | Email delivery powered by Google |
| Google, 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA 94043, United States | |

Comments
Post a Comment